Project #4 - Concurrency Control
项目准备
项目地址:Project #4 - Concurrency Control。
准备工作:阅读 Chapter 18 19,学习 Lecture #15 #16 #17 #18 #19 #20,以及阅读课堂笔记。
项目结构
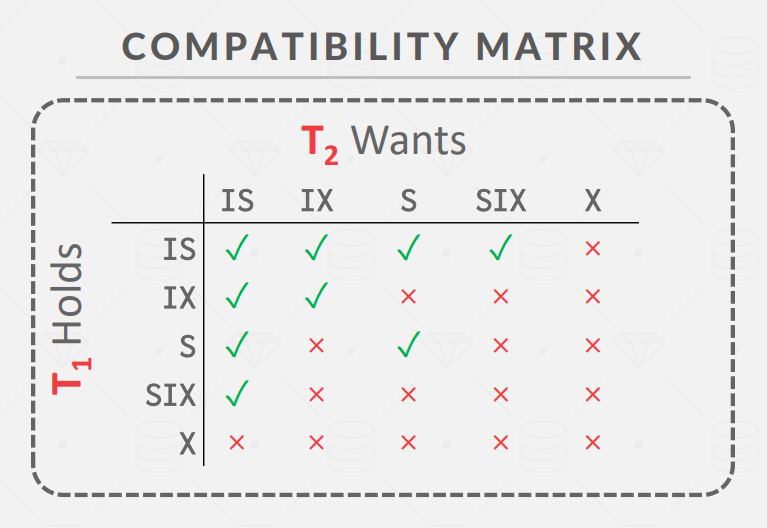
项目的注释中有锁升级的矩阵图,但是没有兼容性的矩阵图,这里贴一下。
Task #1 - Lock Manager
实现
① 比较关键的一个问题是,LockRequestQueue 里面存什么。我之前漏掉 granted_ 成员,导致整个项目理解都有问题。一个请求会经历未获取锁、已获取锁,已释放锁三个过程,LockRequestQueue 存储所有没有被释放的锁请求,即前两个过程。因为之后能否获取锁,需要和之前已经获取的锁做兼容性判断。
② 加锁阶段:
- 代码组织:我们可以根据请求的锁模式来分类讨论,也可以根据事务的锁模式来分类讨论,也可以根据事务是否有锁进行分类讨论。我最后是选择最后一种方式,这样写起来真的简洁。如果当前事务没有该资源的锁,则将请求入队,并且根据该资源是否被其他事务上锁,从而直接拿锁或者进行等待;否则,判断能否进行锁升级。
- 锁升级:
- 根据提示,首先判断请求的锁模式是否和事务的锁模式是否相同,如果相同则直接返回
true。我在这里有个比较疑惑的点,如果请求锁模式的级别低于当前持有的锁模式,应该也可以直接返回true,但是注释中并没有提及,并且线上测试结果告诉我不行,必须抛出异常。似乎是设计的问题,讨论在此,而且这个讨论似乎说的也不完整。 - 然后判断是否可以锁升级,如果可以,我们需要释放之前的锁,并等待获取升级的锁。这两个步骤可以通过修改队列中的
LockRequest实现,将锁模式修改为新的锁模式,将granted_修改为false,然后cv_.wait()即可。关键是条件变量的获取锁的条件如何编写。注意,一定要在等待之前从当前事务的锁集中移除原来的锁,因为线上测试会在等待时检查锁集。
- 根据提示,首先判断请求的锁模式是否和事务的锁模式是否相同,如果相同则直接返回
- 获取锁:如何以 FIFO 的方式获取锁,并且使兼容的锁可以同时获取,以及使锁升级的优先级最高。遍历请求队列,如果当前事务是锁升级请求,则只需判断当前请求是否和已
granted_的请求兼容。如果当前事务不是锁升级请求,并且存在其他事务的锁升级请求,则直接返回false,否则不仅需要判断当前请求是否和已granted_的请求兼容,还需要判断当前请求是否和在该请求之前的未granted_的请求兼容。
③ 解锁阶段:按照注释模拟,需要注意从队列中移除完成的锁请求,并在最后执行 cv_.notify_all()。
④ 事务的 ABORTED 状态:如果事务被中止,那么应该取消该事务所做的操作,事务中止之后会自动调用 TransactionManager::Abort 函数来进行解锁和还原所有写操作。但是如果事务在等待锁的过程中被中止,那么就需要我们手动重置,因为 Abort 函数不会清除未获取锁的请求。步骤如下:在使用条件变量时,额外判断当前事务的状态是否是 ABORTED,如果是则直接退出等待,并从队列中移除该请求,如果是锁升级还要记得重置 upgrading_,最后调用 cv_.notify_all() 并返回 false。
补充
① 一个细节问题,在获取 map 中的 LockRequestQueue 时,我依赖 C++ 在使用 [] 访问会自动创建对象的特性,没有注意到 map 中存的是智能指针,这样默认是创建空指针,结果就会报各种奇怪的错误。
② 表解锁同样需要改变事务的状态,一开始我天真的以为只需要在行解锁的时候改变就行,因为我以为加表锁必定会加行锁,但是不是这样的,可以只加表锁(或许全表扫描就是只加表锁而不加行锁)。
③ 线上测试遇到神奇的错误,pthread_mutex_lock.c:94: _pthread_mutex_lock: Assertion ‘mutex->data.__owner == 0’ failed,而且不是每次测试都会发生。经过排查,发现又是自动补全的锅,导致重复执行 unlock() 操作,有关该错误的讨论在此。
④ 目前似乎不需要使用事务锁,单个事务加锁/解锁是单线程的。
Task #2 - Deadlock Detection
① 构建等待图,使用二重循环遍历 table_lock_map_ 和 row_lock_map_ 来向 waits_for_ 添加从 granted_ == false 请求到 granted_ == true 请求的边。其实这样单纯的加边是比较简单的,但是可能存在锁兼容的情况,这样构成的环是不会造成死锁的,导致误杀事务,不过测试能过就不改代码了。记得加锁。
② 因为可以存在很多环,如果检测顺序不一样,中止的事务可能完全不同,所以 NOTES 中要求我们从最小的事务开始做 DFS,按照从小到大的顺序遍历相邻节点,如果找到环,则中止环中最大的事务。如果事务被中止,则应该从图中删掉连接该事务的边,或者也可以打标记。有坑!!!HasCycle 应该包含什么代码,之前我是把最小事务编号作为参数传递,然后从该事务开始做 DFS 来检测环。但是线上 GraphTest 测试会调用 HasCycle,按照线上测试代码的逻辑,HashCycle 应该包含整个环检测代码,包括排序 waits_for_,排序 GetEdgeList 得到的边集,以及 DFS。特别注意,不要在 HashCycle 中调用 txn_manager_ 的任何方法,因为 GraphTest 测试根本就没创建事务!!!我是调试半天找不到错,才反应过来,非常无语。
③ 最后,从 HasCycle 返回时,删除中止事务的边,然后调用 TransactionManager::Abort 函数中止事务。在消除所有环之后清空 waits_for_。
Task #3 - Concurrent Query Execution
① 非常非常无语!!!就是我在 Task#1 中提到的,高级锁可以包含低级锁的需求,不应该抛出异常,结果测试不给过,Task#3 又需要我兼容这种情况,那么只能在 Executor 代码中特判了。
② 根据提示,should not acquire S/X table lock, grab IS/IX instead,只为表加 IS/IX 锁。
③ 细节问题:行加锁之后再判断行是否删除,这个错误找很长时间才发现;死锁检测在调用 Abort 函数之前,先将事务状态设置为 ABORTED,否则当前事务可能会在之后的解锁过程中被唤醒,触发 LOCK_ON_SHRINKING 异常;实现 Abort 函数时,将恢复阶段放在解锁阶段之前,不然可能会有并发问题。
Leaderboard Task (Optional)
① 初次提交。
| Rank | Submission Name | Update QPS | Count QPS | Weighted QPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 59 | ALEX | 14 | 14 | 14 |
测试结果
1 | !/bin/bash |
项目小结
难点就在项目理解以及代码细节上,Task#1 和 Task#2 被队列和 HashCycle 的理解整晕了,然后要使代码能够在多线程情况下正常运行,一定要注意代码中逻辑的先后顺序!!!实现过程部分参考做个数据库:2022 CMU15-445 Project4 Concurrency Control,Task#1 的解释帮助很大。